
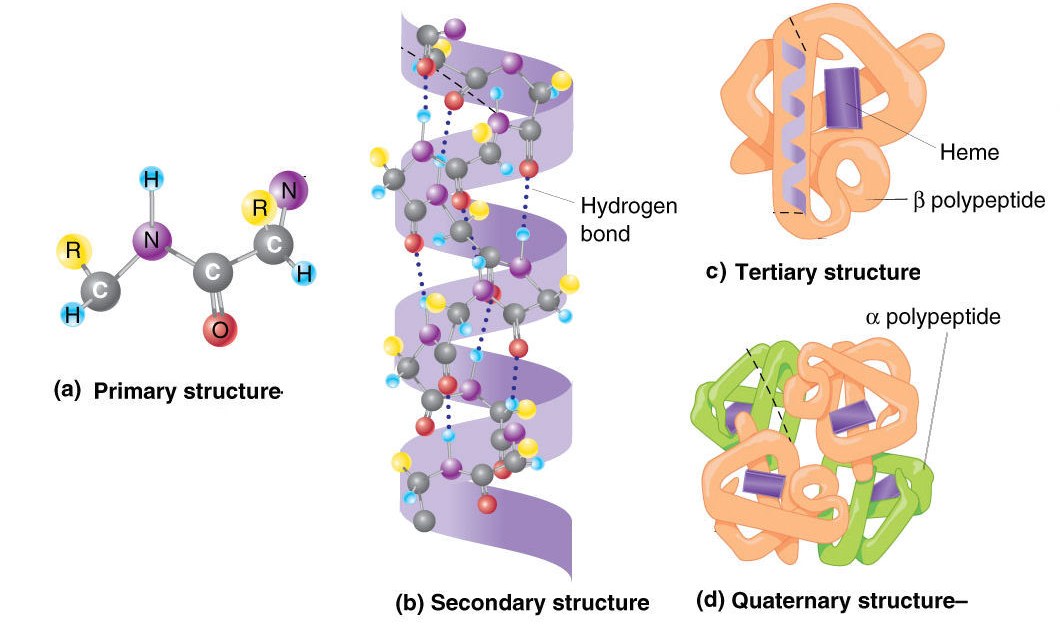
Methionine, alanine, leucine, glutamate, and lysine uncharged (“MALEK” in the amino-acid 1-letter codes) all have especially high helix-forming propensities, whereas proline and glycine have poor helix-forming propensities. The C=O is hydrogen bonded to the N_H of the peptide link four units ahead in the primary structure, while it follows that the N_H is hydrogen bonded to the C=O of the peptide link four units behind.ĭifferent amino-acid sequences have different propensities for forming α-helical structure. Secondly, and most importantly, each peptide link is involved in two hydrogen bonds. Firstly the side chain groups are quite well separated. The alpha helix conformation has a particular stability for two main reasons. The 3_10 helix has a smaller radius, compared to the α-helix, while the π-helix has a larger radius. Other helical structures include the 3_10 helix, which is stabilized by hydrogen bonds of the type (i, i+3) and the π-helix, which is stabilized by hydrogen bonds of the type (i, i+5). The α-helix is not the only helical structure in proteins. This regular pattern gives the α-helix very definite features with regards to the thickness of the coil and the length of each complete turn along the helix axis. Such a hydrogen bond is formed exactly every 4 amino acid residues, and every complete turn of the helix is only 3.6 amino acid residues. This coil is held together by hydrogen bonds between the oxygen of C=O on top coil and the hydrogen of N-H on the bottom coil.
The prediction was confirmed when the first three-dimensional structure of a protein, myoglobin (by Max Perutz and John Kendrew) was determined by X-ray crystallography.Īn α-helix is a right-handed coil of amino-acid residues on a polypeptide chain, typically ranging between 4 and 40 residues. Linus Pauling was the first to predict the existence of α-helices. The most common type of secondary structure in proteins is the α-helix.
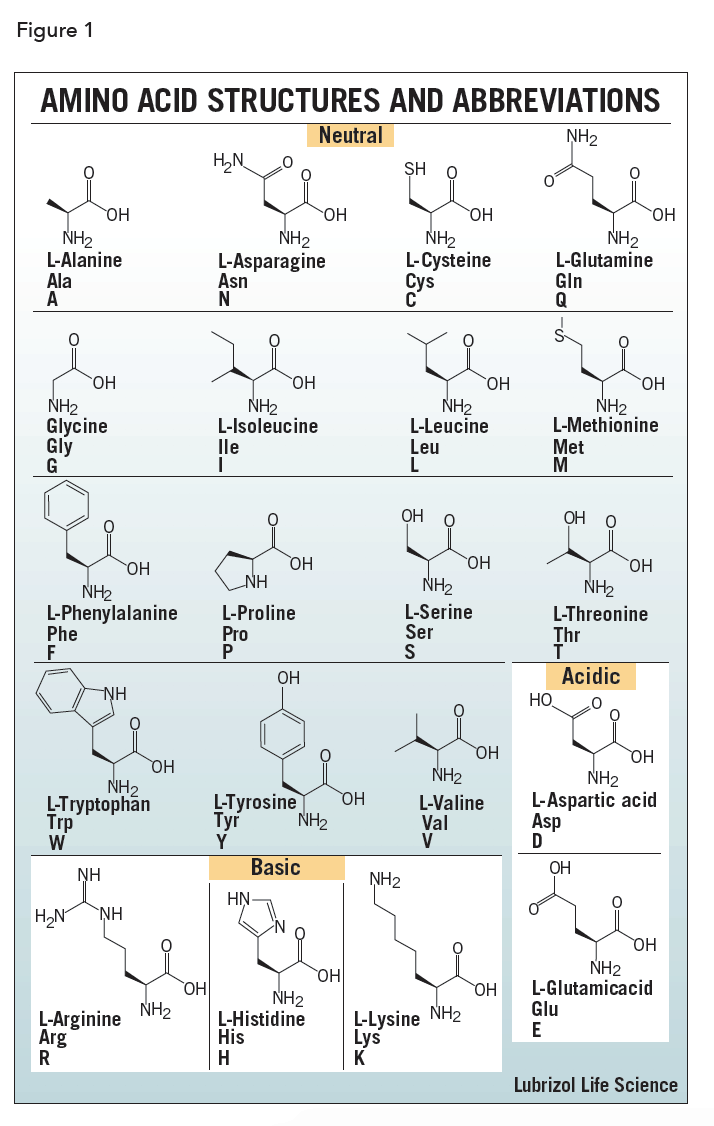
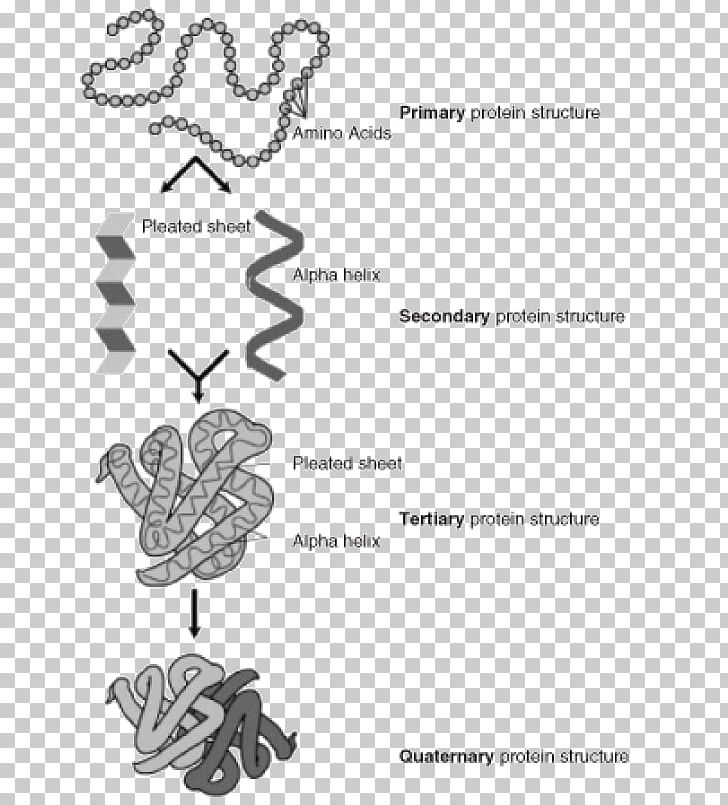
The secondary structures in proteins arise from repeating patterns of similar peptide dihedral angles (φ and Ψ)for successive residues The secondary structures imply the hierarchy by providing repeating sets of interactions between functional groups along the polypeptide backbone chain that creates, in turn, irregularly shaped surfaces of projecting amino acid side chains. Five stranded Rossmann-like folds are arranged in the sequential order 32145.Protein Secondary Structure Prediction-Background theory Overall, the strands are arranged in the order of 321456 (1 = N-terminal, 6 = C-terminal).

This pattern is duplicated once to produce an inverted tandem repeat which contains six strands. The first three strands are connected by α-helices resulting in a beta-alpha-beta-alpha-beta structure. The Rossmann fold is composed of six parallel beta strands that form an extended beta sheet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
